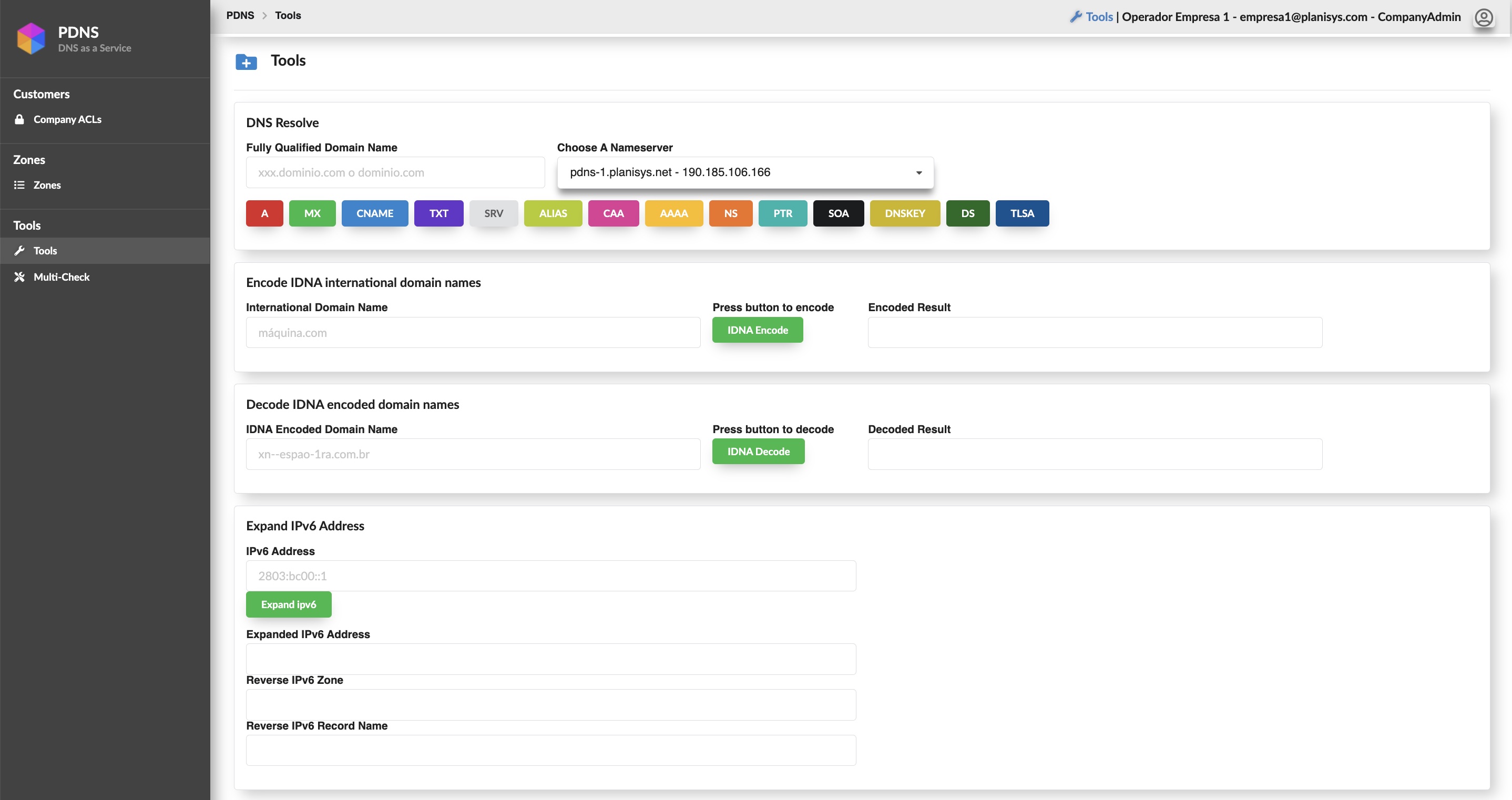
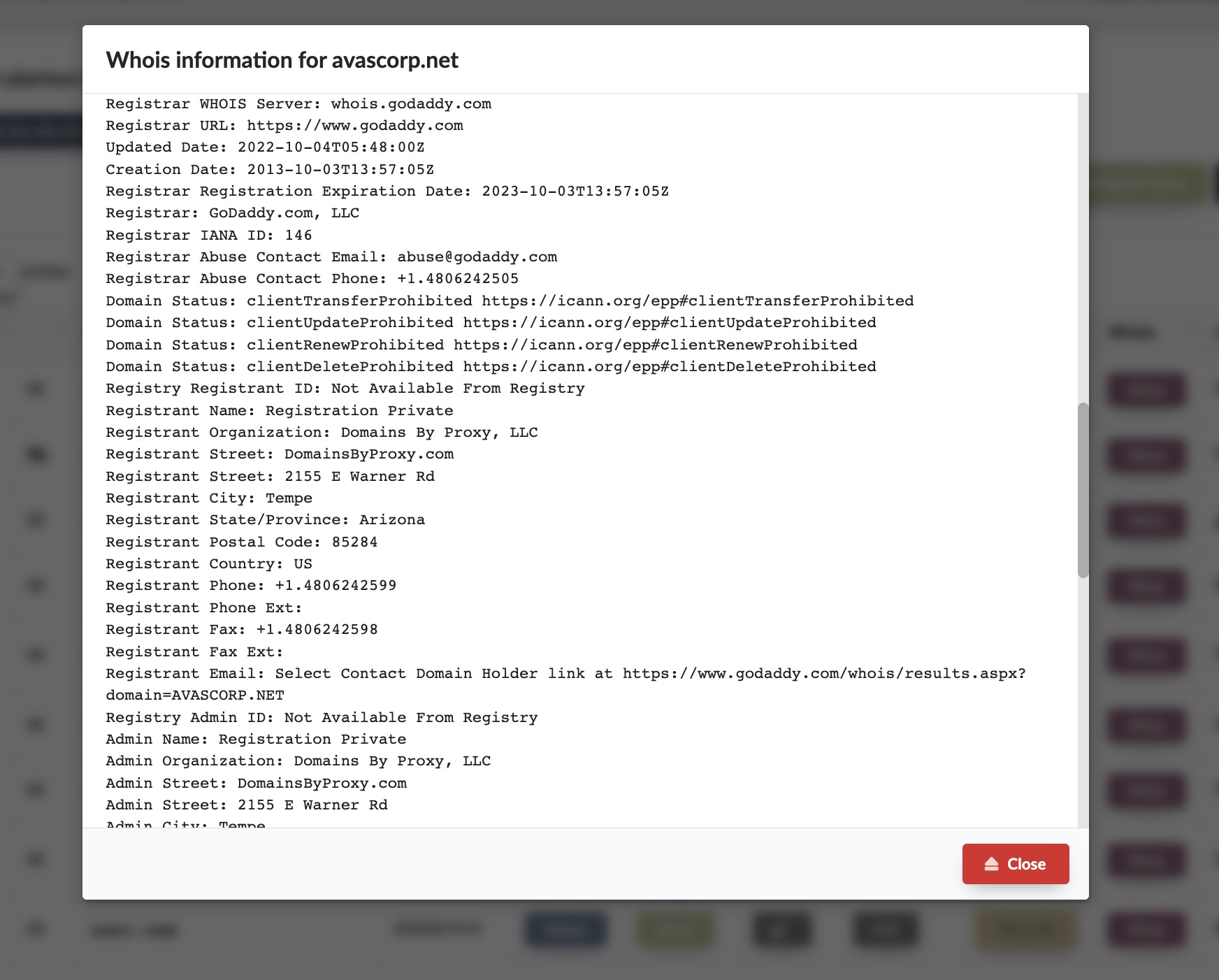
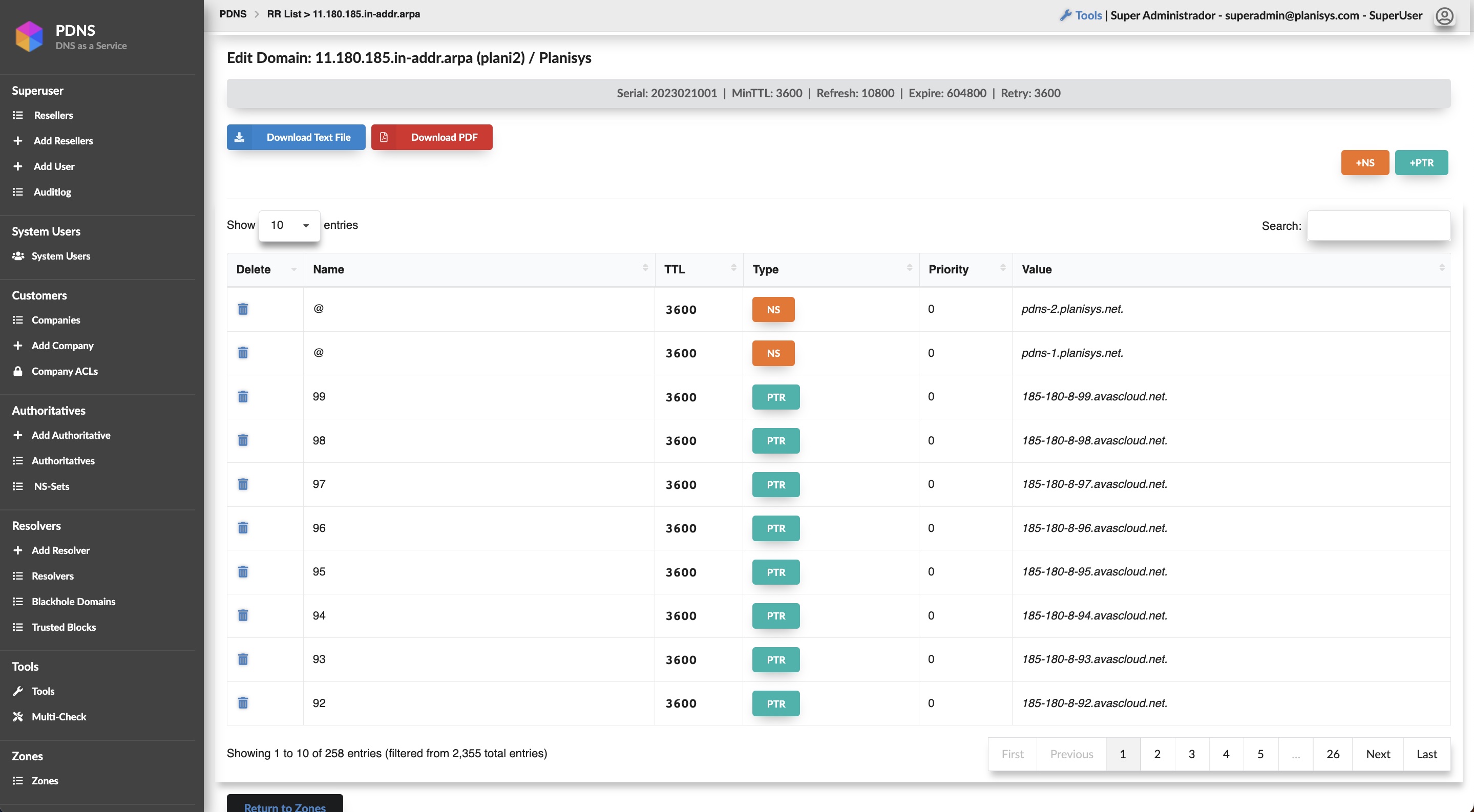
PDNS: DNS as a Service
- Complete Bind9 based solution
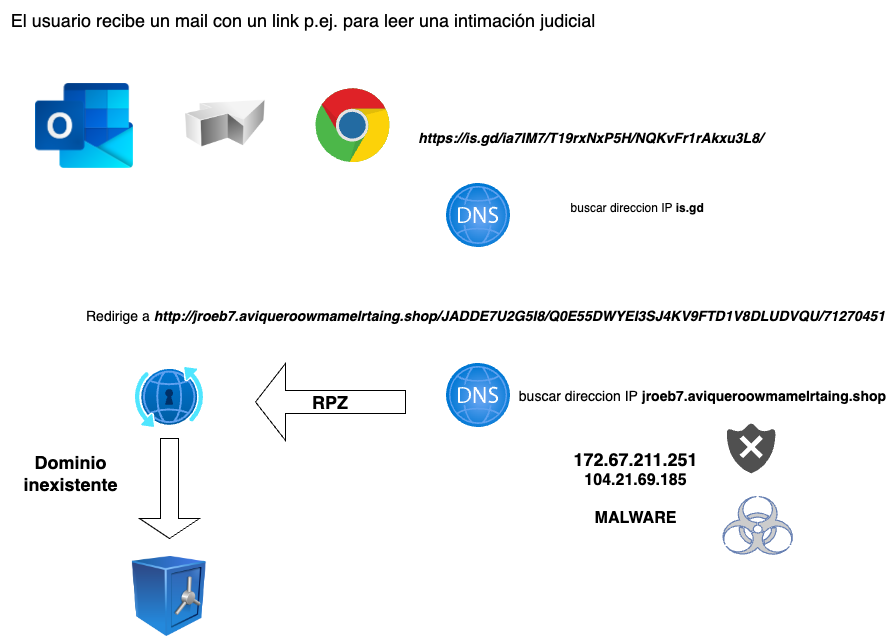
- Recursive DNS-Firewall RPZ (Response Policy Zones) for endpoint security
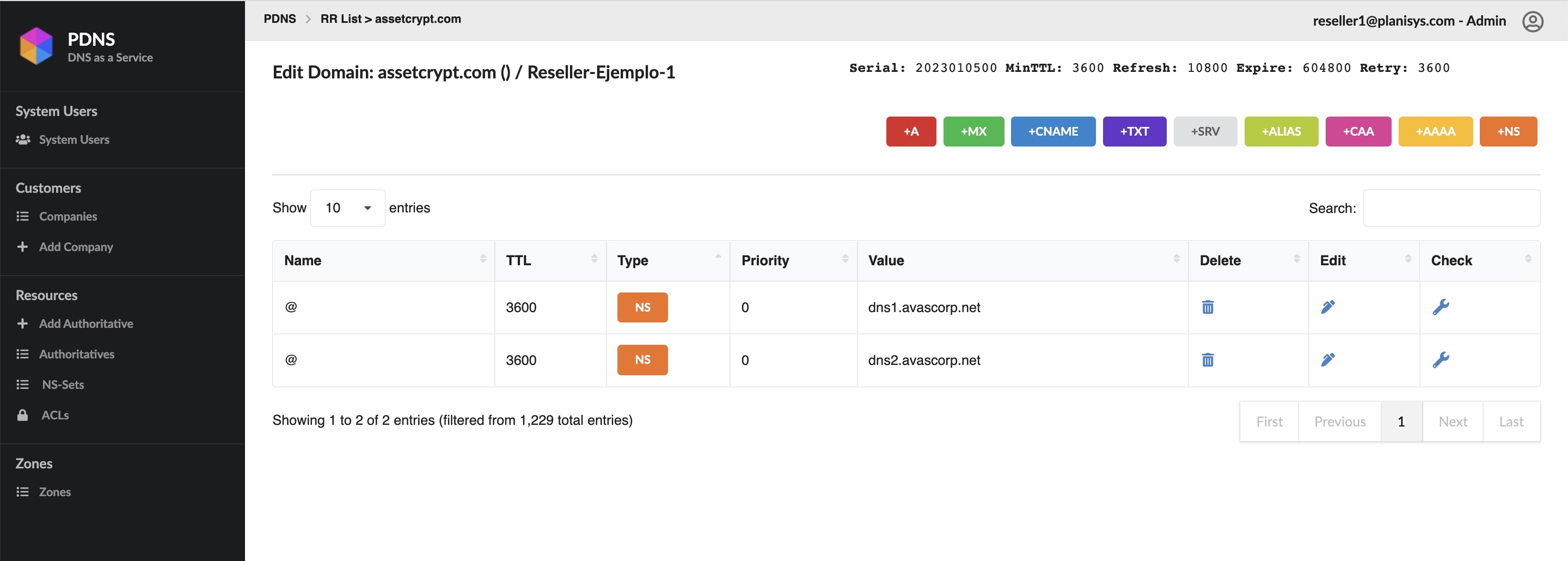
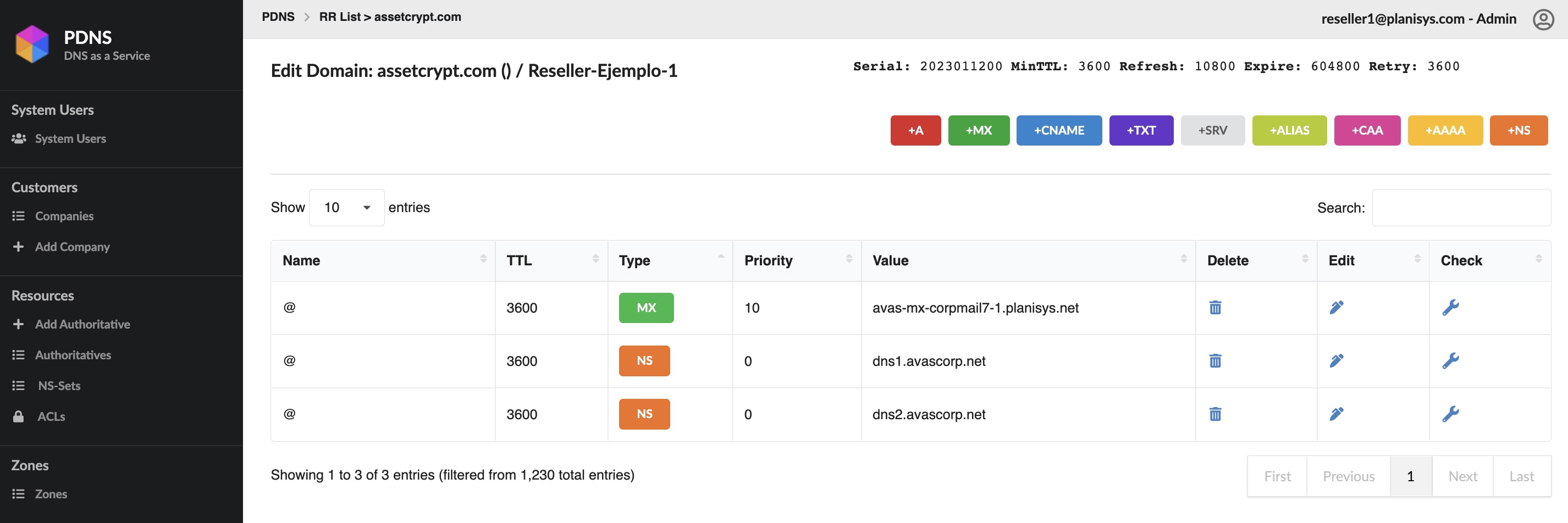
- Authoritative DNS for your Organization
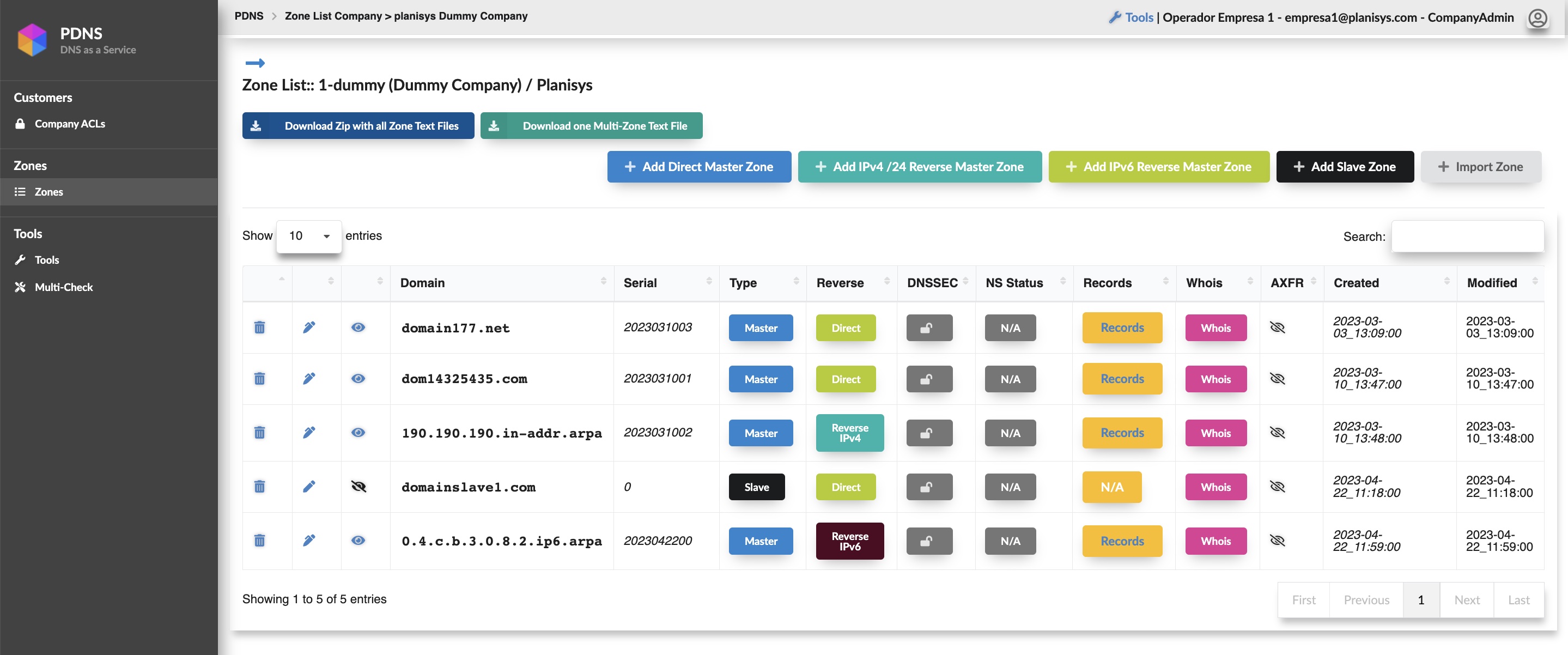
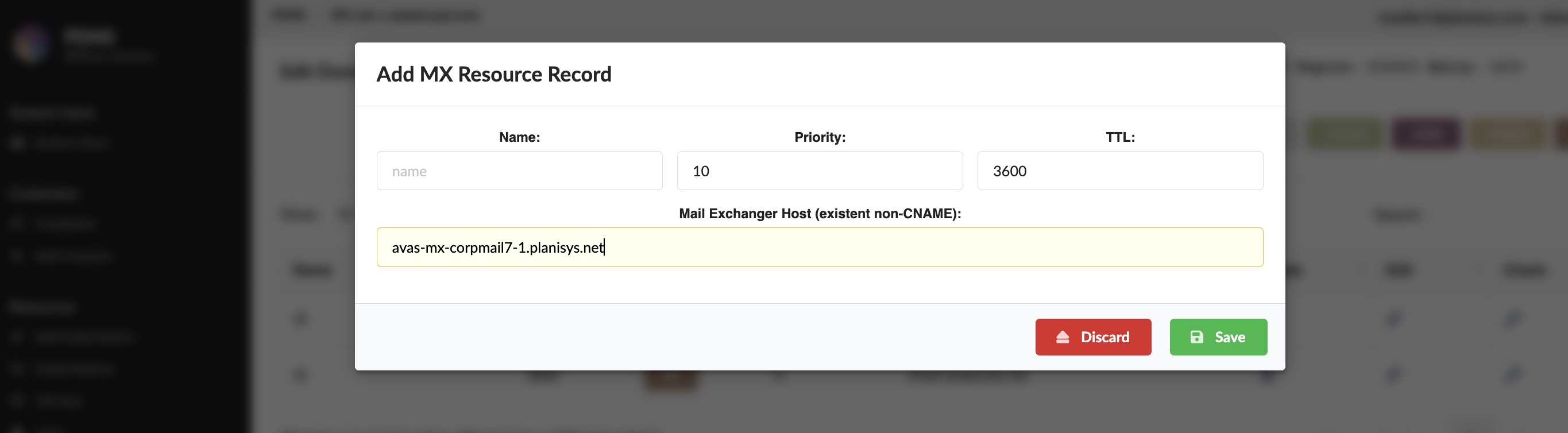
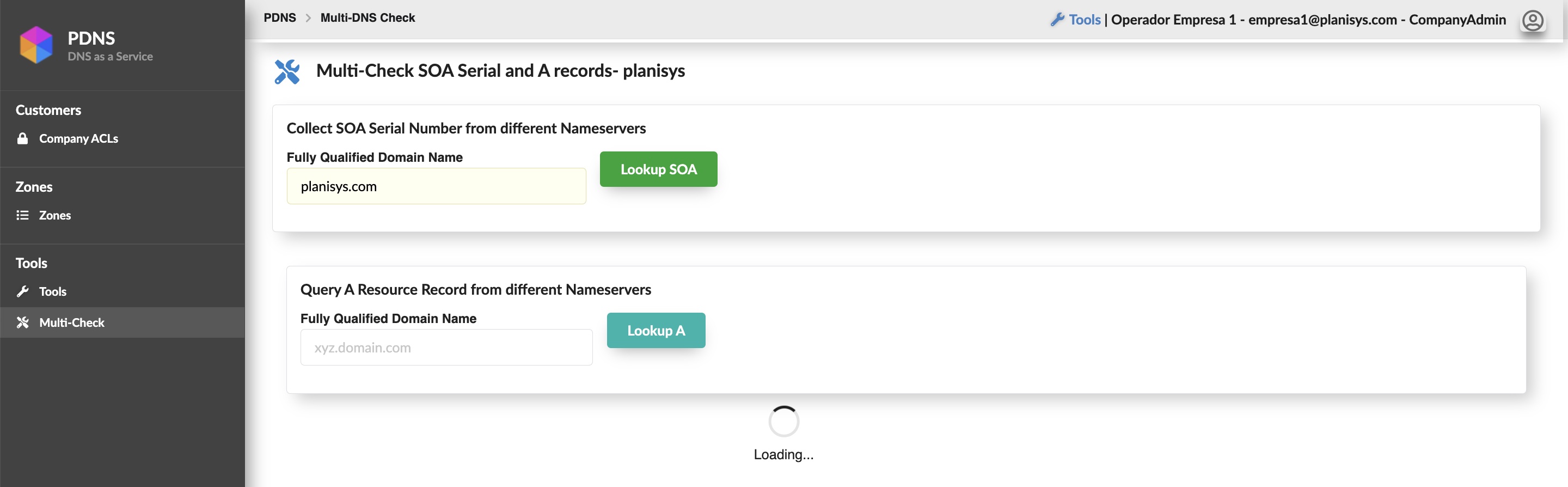
- WebUI and API for DNS
- Antispoofing, Anti-DDoS and Cache Poisoning Controls
- DNSSEC for increased security and brand protection
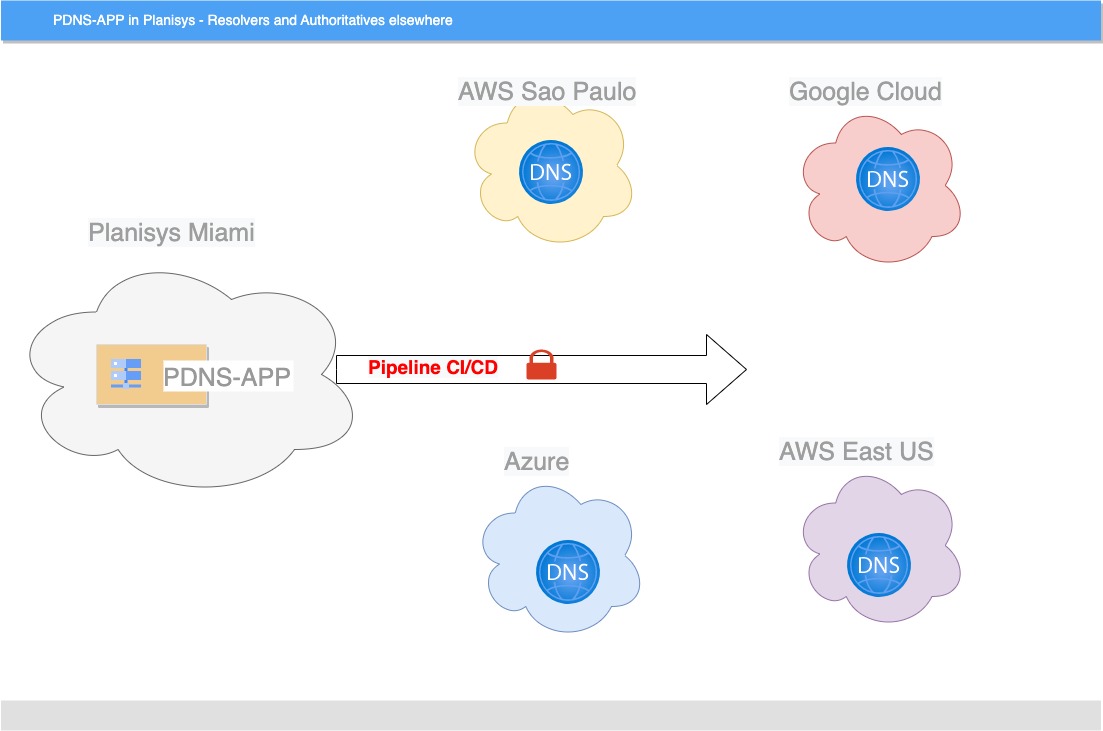
DNS is a critical component behind all Internet applications, websites, e-mail, messaging and e-commerce. We at Planisys have developed the PDNS platform for task automation and full control of the DNS Operation at Service Providers, Financial Institutions and other Organizations requiring a high level of security.
Read about DNS Attacks Read the PDNS Docs